Firewall
The firewall is a simple computer with pfSense installed on it.
pfSense is a FreeBSD based software that is often used to power firewalls. This means that there are some hardware requirements involved:
⚠️ Warning!
- the device must be powered by an AMD64 CPU (because ARM CPUs are not widely supported) and its network interfaces mustn't use Realtek chipsets (Intel chipset are recommended because of compatibility issues).
- we need at least three network interfaces (WAN, LAN and OPT1).
In our case, the hardware doesn't matter because it is installed on a VM.
Description
The firewall has several uses in this architecture:
- Packets filtering: restrict access outwards and inwards using rules applying on specific ports and protocols.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.
- DNS (Domain Name System): hierarchical and distributed name service that provides a naming system for computers, services, and other resources on the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
- Router: acts as a bridge between different networks (here, between the sub-LANs and the WAN).
- NAT (Network Address Translation): method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device (here, rules for HTTP and HTTPS requests for the web server).
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): creates a secure connection on a public network.
- Monitoring and reports: provides tools to monitor the traffic on the network and to generate detailed reports.
- Bandwidth management: controls and limits the bandwidth.
Network interfaces
LAN (Local Area Network) & OPT1
The LAN (and OPT1) interface is connected to our internal private networks. It is responsible for the communication between devices on those private networks.
- IP Addresses: LAN 10.0.0.1, OPT1 10.0.0.9
- Description: Gives access to internet to all devices connected to that interface and applies security rules to protect the local networks.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
The WAN interface is connected to internet. It receives a public IP address from the ISP (Internet Service Provider). On our VM, we configured this interface in NAT, so that it receives an IP address from the host, without having problems with the network configurations at YNOV.
- IP Address: Attributed by DHCP (VM's host)
- Description: Manages the inward and outward traffic, applying the security rules to protect from outside threats.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
The DMZ interface is used to host services reachable from internet, isolating it from the local network (LAN) for security purposes.
- IP Address: 10.0.1.1
- Description: Hosts our webserver which documentation is publicly reachable and applies security rules to limit access to specific services.
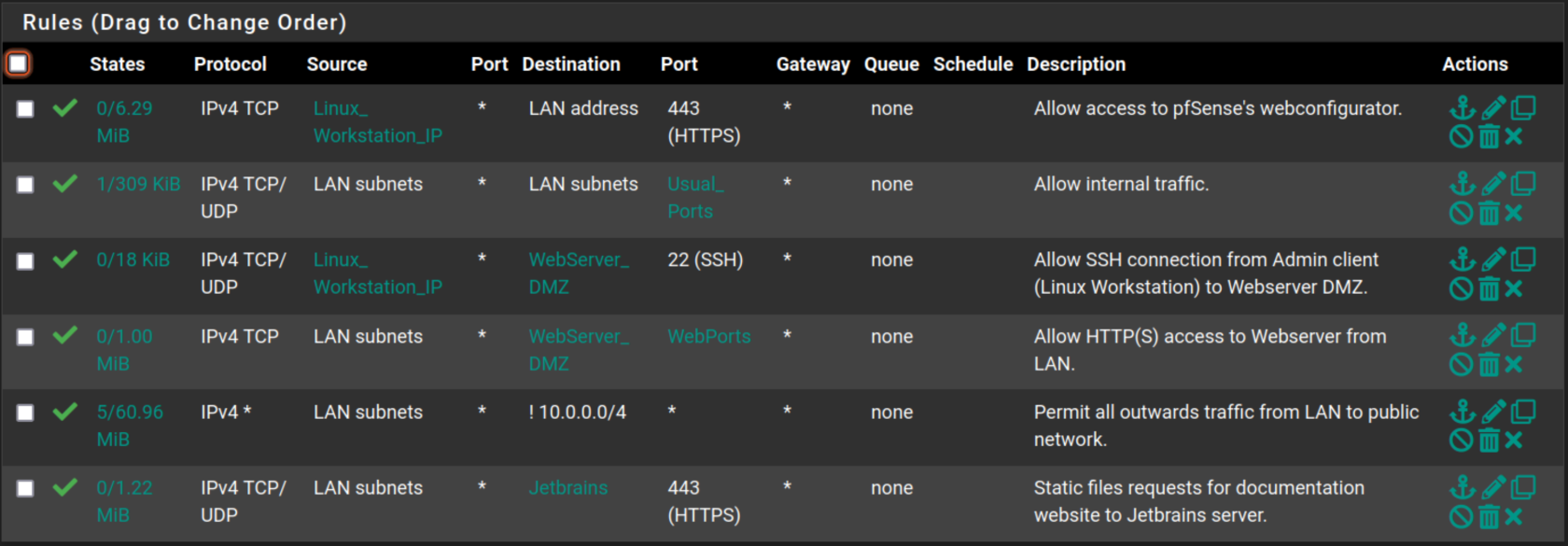
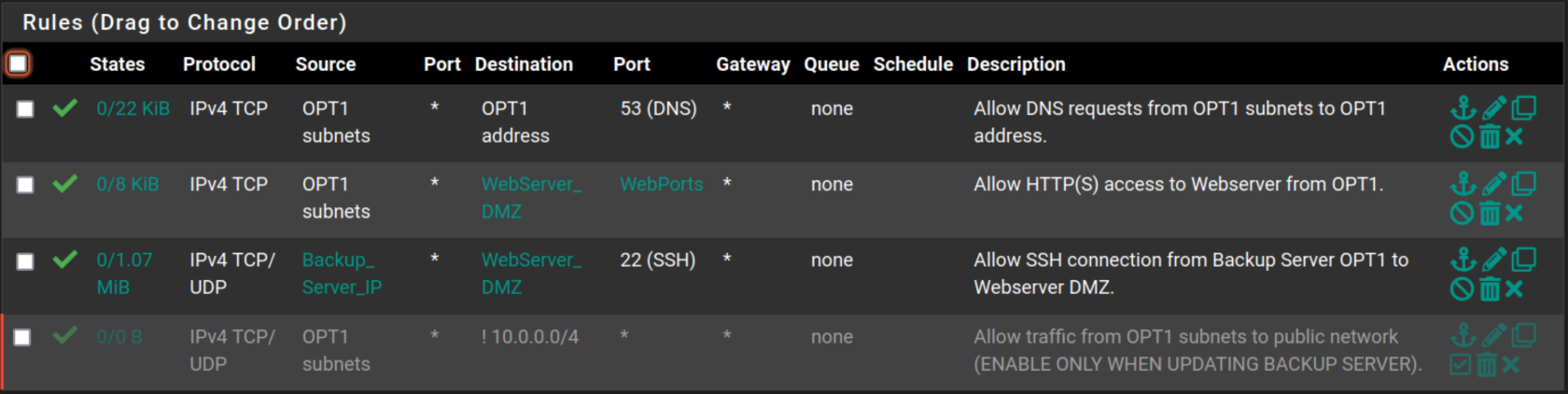
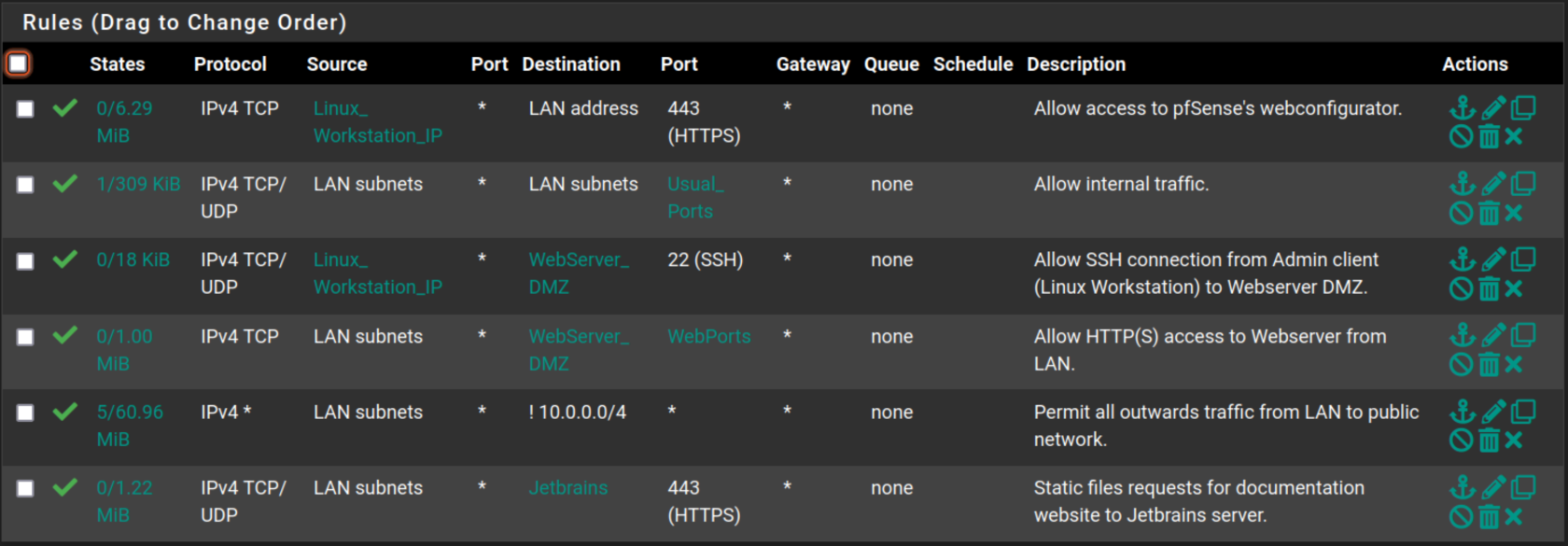
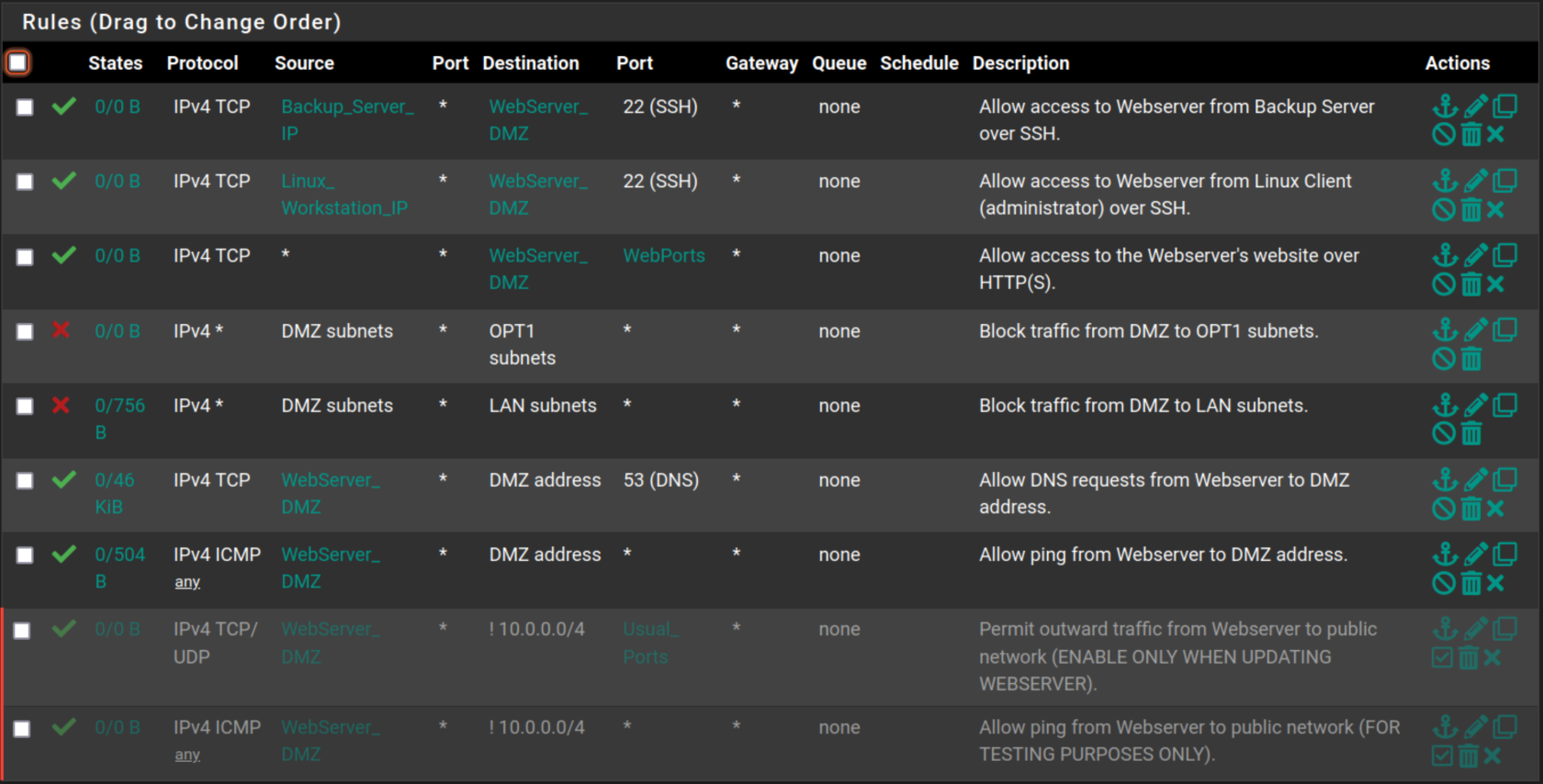
Filtering Rules
LAN
OPT1
WAN
DMZ
Conclusion
The pfSense firewall plays a crucial role in the security of our network infrastructure controlling all traffic between its interfaces (WAN, LAN, OPT1, DMZ) applying security rules that we chose and just presented.
This documentation provides a complete overview of the configurations of pfSense and its filtering rules.
No Comments